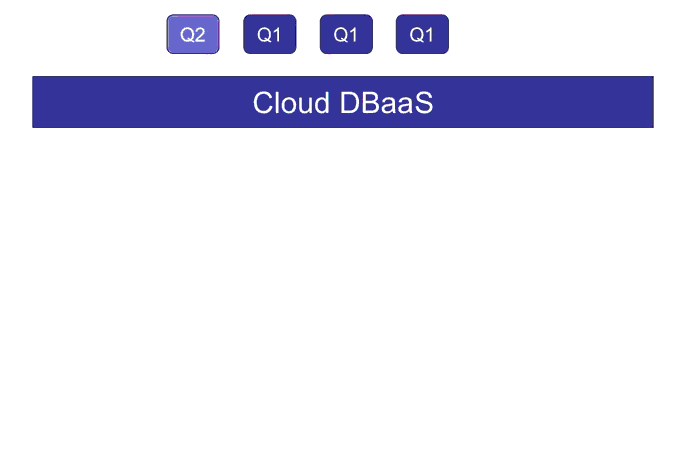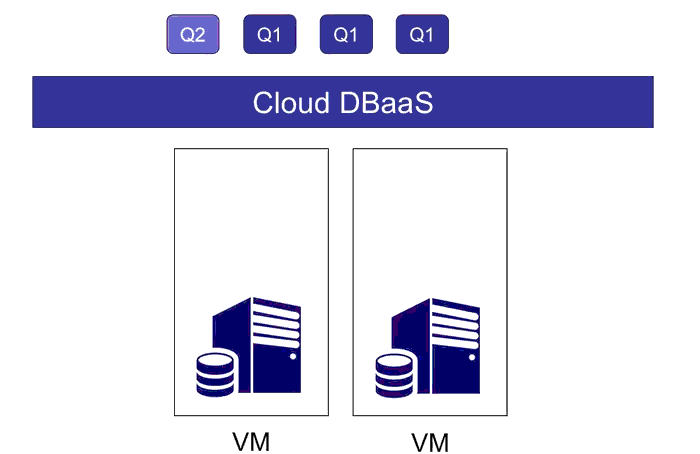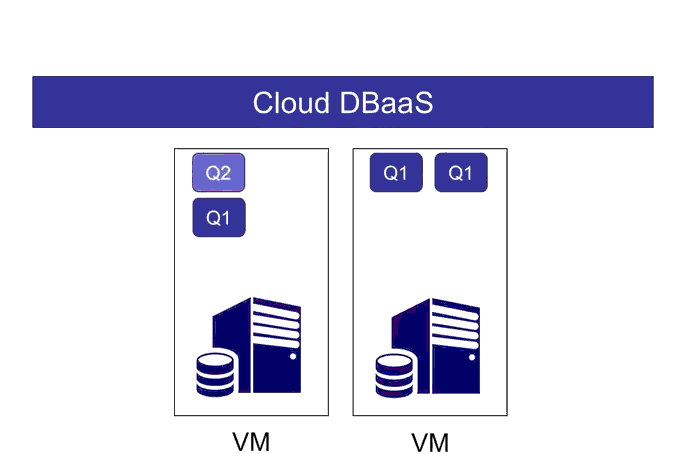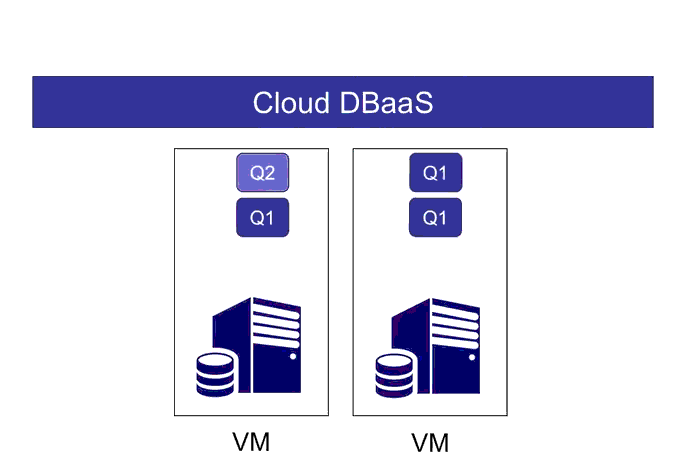
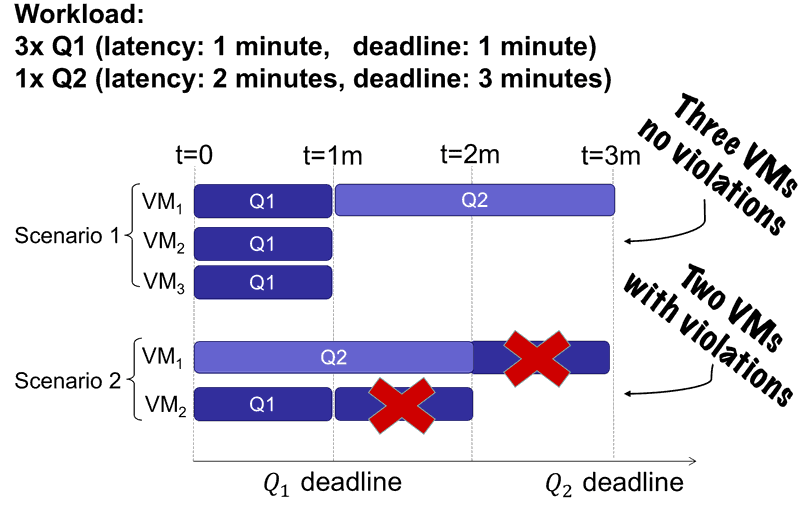
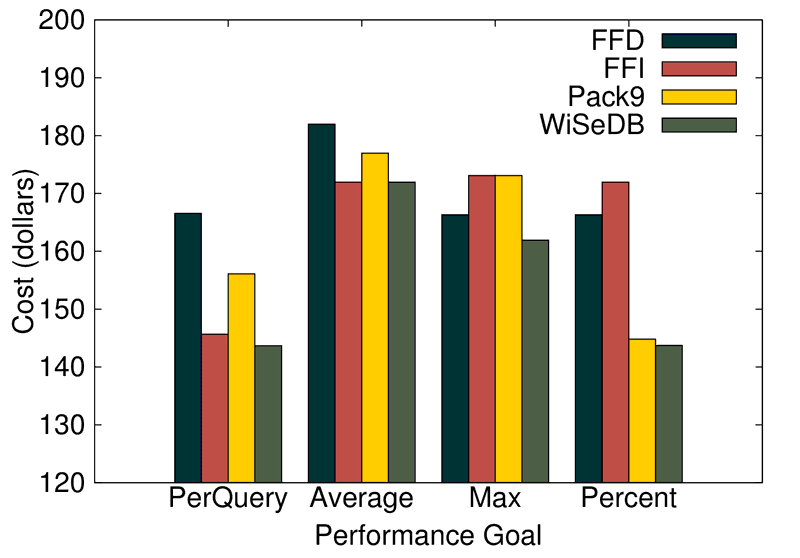
This project contains code for the WiSeDB project, a part of the XCloud project at Brandeis University. This is a Java implemention of the WiSeDB system as described in:
Marcus, Ryan, and Olga Papaemmanoul. "WiSeDB: A Learning-based Workload Management Advisor for Cloud Databases" Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, Volume 9, No. 10 June 2016
Marcus, Ryan, and Olga Papaemmanouil. "Workload Management for Cloud Databases via Machine Learning." Workshop on Cloud Data Management and the IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering, CloudDM. Vol. 16. (2016)
Marcus, Ryan, and Olga Papaemmanouil. "WiSeDB: A Learning-based Workload Management Advisor for Cloud Databases." arXiv preprint arXiv:1601.08221 (technical report, 2016).
Detailed API documentation can be found at the Maven-generated site hosted by Brandeis. You can also watch a "chalk talk" about this research presented at HPE Vertica here.
WiSeDB is designed to assist cloud applications in making three types of decisions:
- Resource provisioning: determining the number of VMs needed to process a workload
- Query placement: determining which query should execute on which VM
- Query scheduling: scheduling the queries within a VM
WiSeDB provides a complete, integrated answer to these problems, and it does so in an SLA-aware way. WiSeDB utilizes machine learning in order to create custom heuristics that are tailored to an application's workload and performance goal.
Imagine you have three types of tasks:
- Task
A, which takes 2 minutes - Task
B, which takes 3 minutes - Task
C, which takes 4 minutes
Imagine you have a workload with 2 As, 2 Bs, and 2 Cs. Your goal (SLA) is to complete all the tasks within 9 minutes. Since you want to minimize the number of VMs you have to rent (to reduce costs), you want to find the fewest number of VMs that can process the workload on time. In this case, the workload management problem is equivalent to the bin packing problem and is thus NP-Hard.
One possible solution, using the traditional FFD heuristic, is:
- VM1:
[C, C](8 minutes) - VM2:
[B, B, A](8 minutes) - VM3:
[A, A](4 minutes)
... which uses three virtual machines. However, the solution we really want is:
- VM1:
[C, B, A](9 minutes) - VM2:
[C, B, A](9 minutes)
... which uses only two virtual machines.
WiSeDB is a system that uses machine learning in order to generate customized heuristics that are tailored to your application's specific workload and performance goals. When given this workload specification and workload goal, WiSeDB learns a strategy of "place an instance of C, then B, then A, then create a new VM and repeat", which produces the desired outcome.
Of course, WiSeDB does not always find an optimal solution, but in our experiments we find that it always outperforms standard heuristics.
More complicated scenarios can emerge when the SLA changes, for example, to have different deadlines for different query types, to restrict the average performance of a query, or to enforce a percentile-based constraint (e.g. 90% of the queries must complete within 10 minutes).
WiSeDB may not learn a heuristic that is substantially better than a human-crafted default for a particular constraint, but it will match or slightly outperform them. For more information, see the papers.
// first, we build a map that tells us how long each of our
// query types takes to process on different VMs.
// here, we create type 1 which takes 20 seconds, type 2
// which takes 30 seconds, and type 3 that takes 40 seconds on a
// t2.small machine.
Map<Integer, Map<VMType, Integer>> latency = new HashMap<>();
Map<VMType, Integer> forMachine = new HashMap<>();
forMachine.put(VMType.T2_SMALL, 20000);
latency.put(1, forMachine);
forMachine = new HashMap<>();
forMachine.put(VMType.T2_SMALL, 30000);
latency.put(2, forMachine);
forMachine = new HashMap<>();
forMachine.put(VMType.T2_SMALL, 40000);
latency.put(3, forMachine);
// here, we specify the IOs used by each task
Map<Integer, Map<VMType, Integer>> ios = new HashMap<>();
forMachine = new HashMap<>();
forMachine.put(VMType.T2_SMALL, 10);
ios.put(1, forMachine);
forMachine = new HashMap<>();
forMachine.put(VMType.T2_SMALL, 10);
ios.put(2, forMachine);
forMachine = new HashMap<>();
forMachine.put(VMType.T2_SMALL, 10);
ios.put(3, forMachine);
// here, we create the workload specification,
// which gives the latency data, the IO data,
// the machine types we want to make available,
// and the SLA.
WorkloadSpecification wf = new WorkloadSpecification(
latency,
ios,
new VMType[] { VMType.T2_SMALL },
new MaxLatencySLA(60000 + 91000, 1));
// here, we construct a training set of 5000 workloads of size
// 10 in order to train our model.
String training = WiSeDBUtils.constructTrainingData(wf, 5000, 10).get();
// here we build our workload (two instances of each query type)
Map<Integer, Integer> queryFreqs = new HashMap<>();
queryFreqs.put(1, 2);
queryFreqs.put(2, 2);
queryFreqs.put(3, 2);
// here we use WiSeDB to get our workload management strategy
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(training.getBytes());
List<AdvisorAction> a = WiSeDBUtils.doPlacement(bis, wf, queryFreqs);
System.out.println(a);Output:
[[START t2.small(3) (0)], [ASSIGN 3], [ASSIGN 2], [ASSIGN 1], [START t2.small(3) (0)], [ASSIGN 3], [ASSIGN 2], [ASSIGN 1]]
WiSeDB is "research-ware", and is probably filled with bugs, undocumented features, and general trouble. It is GPLv3 licensed.
This research was funded by NSF IIS 1253196.